Graph Neural Networks
Graph Neural Networks(GNN) are a powerful tool for solving problems on graph-structured inputs.
GNNs are a super exciting sub-area of machine learning that is getting a lot of attention and activity and some impressive
results recently.
Google team recently used the molecular structure of compounds along with GNNs to predict their aroma
and showed that, that significantly out performed prior methods. GNNs are a broad topic of knowledge. Graphs in general in the context of
machine learning. [8]
This article explains the basics of Graph Neural Networks, and their usages in the context of Program Representation and Graph matching.
Graph Neural networks are an extension to traditional neural networks that
take full advantage of the graph structure.
What is a graph? </br>
A graph (G) is a set of nodes/vertices (V) connected by directed/undirected edges (E). We can denote the graph as G (V,E) Nodes and edges typically come from some expert knowledge or intuition about the problem. Graphs can be;
- Atoms in molecules
- Users in a social network
- Transportation system or a distribution network, or traffic network
- Neurons in the brain
- A computer program
- A computer network
With machine learning there are multiple tasks that one can carry out on a graph
- Node classification: Predict the type of given node.
Examples include identifying fake users in a social media platform or any other
rating system like Google Maps or Amazon Prime </br>

- Link prediction: Predict whether 2 nodes in a network are likely to have a link.
Link prediction has uses in friend recommendation, movie recommendation,
knowledge graph completion (like associativity between good/bad drugs, and their side effects),
metabolic network reconstruction </br>

- Community detection: Identify densely linked clusters of nodes. Community detection has applications in fraud detection
- Network similarity: How similar are two (sub)networks. This could be used to identifying similar code blocks in a computer programme.
GNN recommendation (PinSage) - Runs in pinterest, Used in Uber eats for food recommendation Customer x buys product a, customer y buys products a and b Now the recommender system should recommend product b to the customer x
How to define similarity - in a recommender system
- Content based: User and item features, the words that describe the user or the item
- Graph based: User-item interactions, in the form of graph/network structure
Heterogeneous GNN (Decagon) - predic side effects of drugs Goal-directed generation (GCPN) - molecule generation
Message passing in graph neural networks and node classification
The idea of message parsing in a graph network is a powerful concept because a lot of the algorithms can be understood from that perspective. In simple terms a node in a graph can send and receive messages along its edges/connections with its neighbors. This is the essence of label propagation algorithms.
Graph/Node Representation Learning
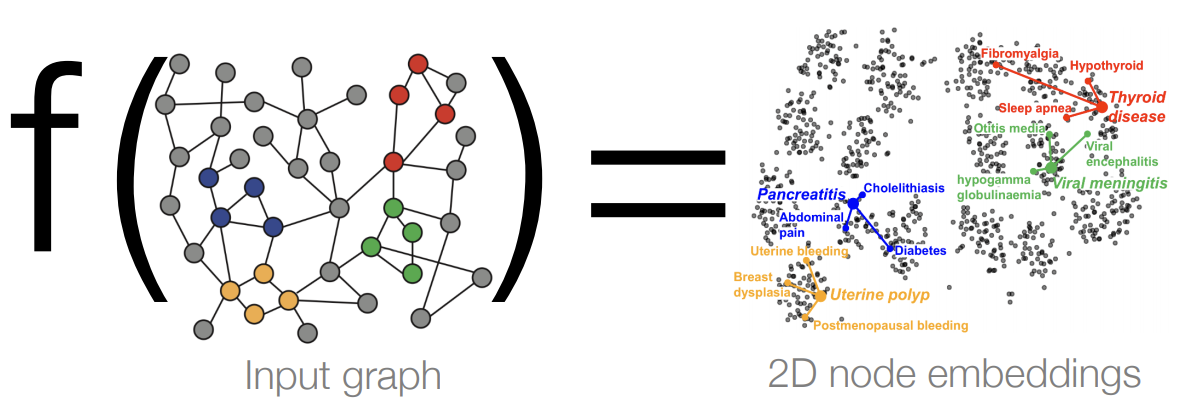
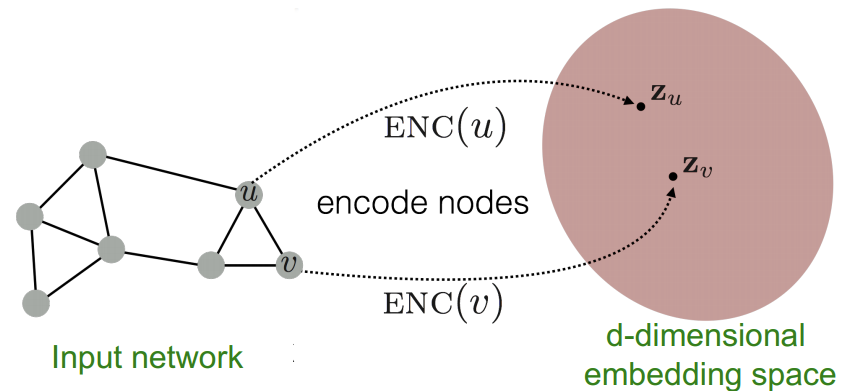
In order to use the graphs in neural network setting, we need to embed the graphs in d-dimensional space such that similar nodes in the graph are embedded close together, i.e. dissimilar nodes in the graph should be embedded far apart in the embedding space.
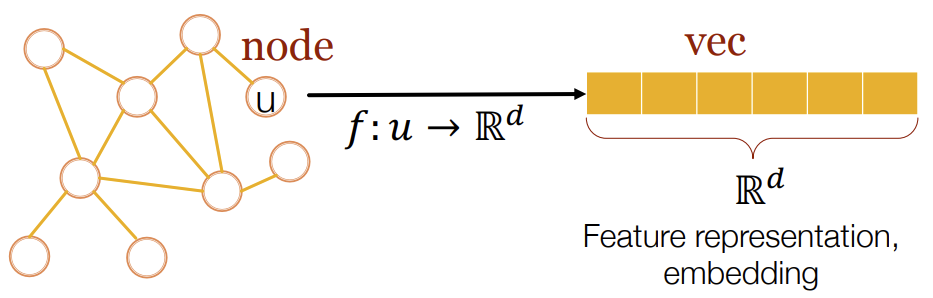
Therefore, an encoding function is needed such that once graph nodes are encoded, the similarity in the graph space is approximated in the embedding space.
Graph Neural Networks
Below are some examples of Graph Neural Networks
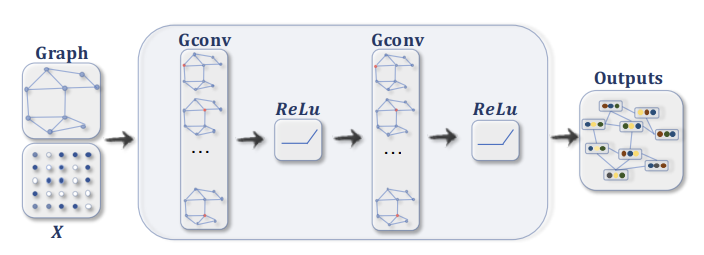 “A ConvGNN with multiple graph convolutional layers. A graph convolutional layer encapsulates each node’s hidden representation by aggregating
feature information from its neighbors. After feature aggregation, a non-linear
transformation is applied to the resulted outputs. By stacking multiple layers,
the final hidden representation of each node receives messages from a further
neighborhood.” 4
“A ConvGNN with multiple graph convolutional layers. A graph convolutional layer encapsulates each node’s hidden representation by aggregating
feature information from its neighbors. After feature aggregation, a non-linear
transformation is applied to the resulted outputs. By stacking multiple layers,
the final hidden representation of each node receives messages from a further
neighborhood.” 4
 “A ConvGNN with pooling and readout layers for graph classification
5. A graph convolutional layer is followed by a pooling layer to coarsen
a graph into sub-graphs so that node representations on coarsened graphs
represent higher graph-level representations. A readout layer summarizes the
final graph representation by taking the sum/mean of hidden representations
of sub-graphs.” 4
“A ConvGNN with pooling and readout layers for graph classification
5. A graph convolutional layer is followed by a pooling layer to coarsen
a graph into sub-graphs so that node representations on coarsened graphs
represent higher graph-level representations. A readout layer summarizes the
final graph representation by taking the sum/mean of hidden representations
of sub-graphs.” 4
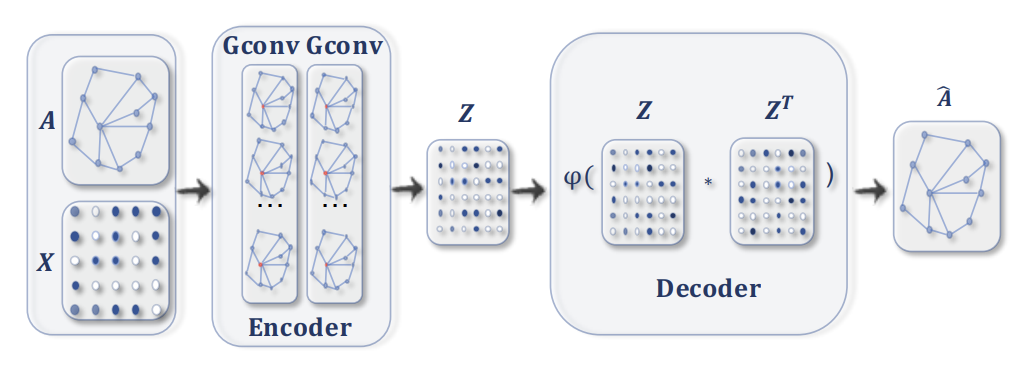 “ A GAE for network embedding [6]. The encoder uses graph convolutional
layers to get a network embedding for each node. The decoder computes the
pair-wise distance given network embeddings. After applying a non-linear
activation function, the decoder reconstructs the graph adjacency matrix. The
network is trained by minimizing the discrepancy between the real adjacency
matrix, and the reconstructed adjacency matrix.” 4
“ A GAE for network embedding [6]. The encoder uses graph convolutional
layers to get a network embedding for each node. The decoder computes the
pair-wise distance given network embeddings. After applying a non-linear
activation function, the decoder reconstructs the graph adjacency matrix. The
network is trained by minimizing the discrepancy between the real adjacency
matrix, and the reconstructed adjacency matrix.” 4
 “A STGNN for spatial-temporal graph forecasting [7]. A graph convolutional layer is followed by a 1D-CNN layer. The graph convolutional layer
operates on A and X(t)
to capture the spatial dependency, while the 1D-CNN
layer slides over X along the time axis to capture the temporal dependency.
The output layer is a linear transformation, generating a prediction for each
node, such as its future value at the next time step.” 4
“A STGNN for spatial-temporal graph forecasting [7]. A graph convolutional layer is followed by a 1D-CNN layer. The graph convolutional layer
operates on A and X(t)
to capture the spatial dependency, while the 1D-CNN
layer slides over X along the time axis to capture the temporal dependency.
The output layer is a linear transformation, generating a prediction for each
node, such as its future value at the next time step.” 4
References
“Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering,” in Proc. of NIPS, 2016, pp. 3844–3852.
[6]: T. N. Kipf and M. Welling,
“Variational graph auto-encoders,” NIPS Workshop on Bayesian Deep Learning, 2016.
[7]: B. Yu, H. Yin, and Z. Zhu,
“Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks: A deep learning framework for traffic forecasting,” in Proc. of IJCAI, 2018, pp. 3634–3640.
[8]: B.S. Lengeling1*, J.N. Wei1, B.K. Lee1 , R.C Gerkin , A.A. Guzik , and A.B. Wiltschko,”Machine Learning for Scent: Learning Generalizable Perceptual Representations of Small Molecules”